Bilingualism is increasingly recognized as an asset in today’s globalized world. As students navigate diverse linguistic environments, the ability to speak more than one language offers significant advantages in education and beyond. This article explores the numerous benefits of bilingualism in language education, highlighting cognitive, social, and academic advantages.
Understanding Bilingualism
What is Bilingualism?
Bilingualism refers to the ability to communicate fluently in two or more languages. This can take various forms, from being equally proficient in both languages to having a dominant language with varying levels of proficiency in the other.
Types of Bilingualism
- Simultaneous Bilingualism: This occurs when a child learns two languages from birth.
- Sequential Bilingualism: This occurs when a second language is learned after the first language is already established.
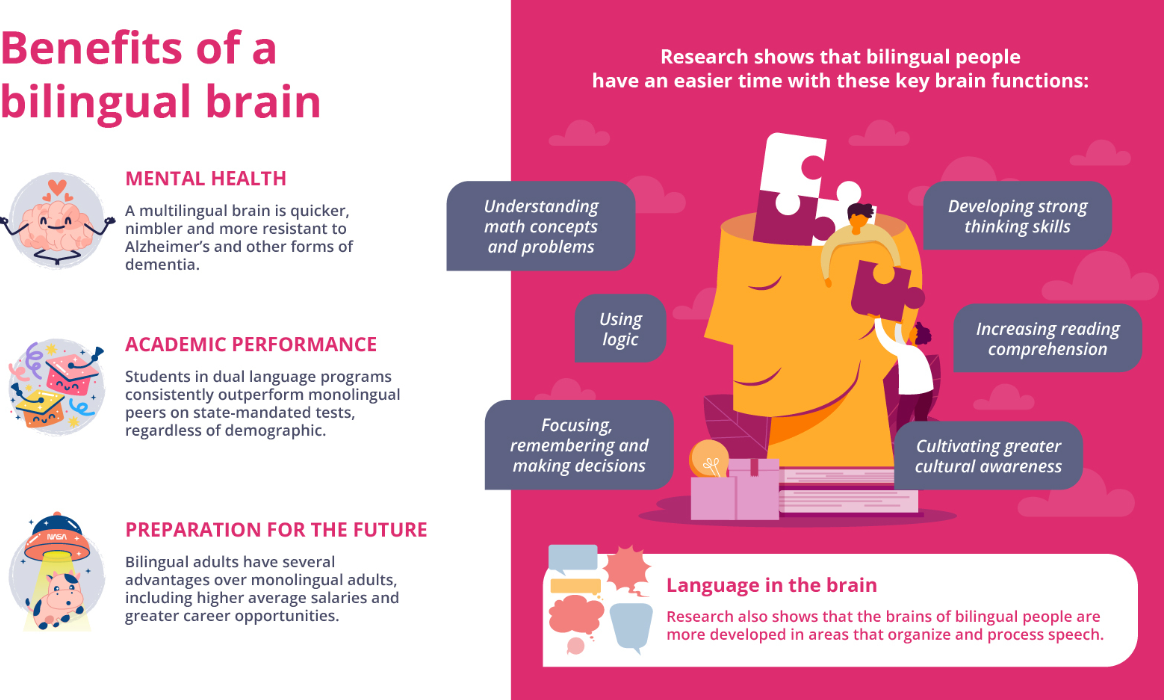
Cognitive Benefits of Bilingualism
1. Enhanced Cognitive Flexibility
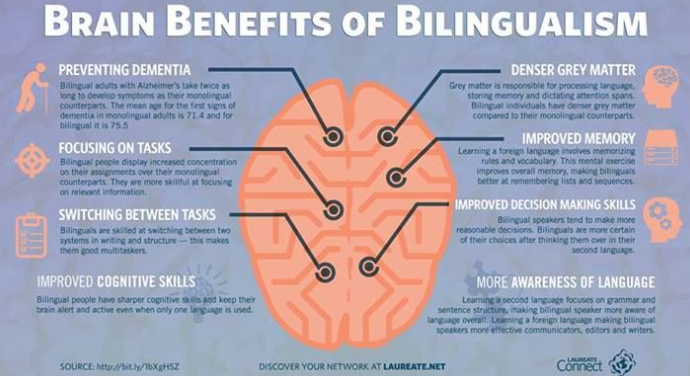
Bilingual individuals often demonstrate greater cognitive flexibility. This means they can switch between tasks and thoughts more easily, which enhances problem-solving skills.
2. Improved Executive Function
Research indicates that bilingualism can strengthen executive function skills. These include:
- Attention Control: The ability to focus on relevant information while ignoring distractions.
- Working Memory: The capacity to hold and manipulate information in mind.
- Cognitive Inhibition: The skill to suppress responses that are not relevant to the task at hand.
3. Better Multitasking Abilities
Bilingual individuals tend to excel at multitasking. The practice of switching between languages helps them manage multiple tasks more effectively.
4. Delay in Cognitive Decline
Studies suggest that bilingualism may delay the onset of age-related cognitive decline and dementia. The mental exercise involved in switching languages appears to contribute to greater cognitive reserve.
Social Benefits of Bilingualism
1. Improved Communication Skills
Bilingual individuals are often more adept at understanding nuances in communication. They can appreciate cultural contexts and subtleties in language, enhancing their social interactions.
2. Cultural Awareness and Sensitivity
Being bilingual often means being immersed in multiple cultures. This exposure fosters greater cultural awareness and sensitivity, essential skills in our interconnected world.
3. Expanded Social Networks
Bilingual individuals can connect with a wider range of people. This can lead to enriched social interactions and opportunities for collaboration.
4. Enhanced Empathy
The ability to communicate in multiple languages can enhance empathy. Bilingual individuals often develop a deeper understanding of others’ perspectives and experiences.
Academic Benefits of Bilingualism
1. Improved Academic Performance
Research has shown that bilingual students often outperform their monolingual peers in standardized tests. This is particularly evident in areas such as reading comprehension and mathematics.
2. Enhanced Language Skills
Bilingualism promotes a better understanding of language structure and function. Bilingual students tend to have a more profound grasp of grammar, vocabulary, and syntax in both languages.
3. Greater Metalinguistic Awareness
Bilingual students develop metalinguistic awareness, the ability to think about and analyze language. This skill can enhance literacy and overall academic performance.
4. Access to Diverse Learning Resources
Bilingual students have access to a broader range of learning materials. They can utilize resources in both languages, enriching their educational experience.
Challenges of Bilingualism in Education
1. Language Proficiency Balance
Maintaining proficiency in both languages can be challenging. Without consistent practice, students may experience a decline in one language, known as language attrition.
2. Limited Resources
In some educational systems, resources for bilingual education may be limited. This can hinder the effectiveness of language instruction.
3. Social Stigma
Bilingual students may face social stigma or pressure to conform to a dominant language. This can lead to feelings of insecurity or reluctance to use their bilingual skills.
4. Curriculum Constraints
Standardized testing and curriculum requirements may prioritize one language over another, potentially disadvantaging bilingual students.
Best Practices for Supporting Bilingualism in Education
1. Foster a Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive environment that values bilingualism is essential. Schools should promote the use of both languages and celebrate cultural diversity.
2. Implement Dual Language Programs
Dual language programs can provide structured support for bilingual students. These programs offer instruction in both languages, allowing students to maintain and develop proficiency.
3. Encourage Family Involvement
Families play a crucial role in supporting bilingualism. Encourage parents to use both languages at home and engage in activities that promote language use.
4. Provide Professional Development for Educators
Educators should receive training on effective bilingual teaching strategies. This can help them create inclusive classrooms that meet the needs of bilingual students.
5. Leverage Technology
Technology can be a powerful tool for supporting bilingual education. Language learning apps, online resources, and virtual language exchange programs can enhance language acquisition.
